The supply chain tech market has been evolving rapidly in recent years. Numerous software and hardware companies are entering the market with supply chain technology, which is bringing about a major shift in business operations.
Real entrepreneurship is driving supply chain technology trends, but it's still questionable whether new technologies can truly support your business. For experts in logistics and the supply chain market, innovations always bring uncertainty. This is the reason why many future technologies still require years before they will be fully adaptable in the supply chain.
We will explain the tech supply chain and how new supply chain technology can bring positive change to your business without disrupting your current operations. Frankly speaking, what deserves attention is how companies should provide solutions without interrupting ongoing operations. Let's examine technologies in supply chain management closely and investigate where actual efficiency can be found.
Getting on the journey with supply chain technology
While the topic of this article promises to deliver more about emerging technologies, it's important to note that changes in the supply chain don't happen overnight. Companies with well-established business processes will use extensive procurement to adapt to supply chain digital transformation technologies. Sometimes, it can take a few years before one goes live.
On the other hand, small and medium-sized businesses will seek cost-efficient and faster solutions to comply with these technologies, especially if their procurement processes aren't entirely in place. They may require assistance in choosing the right partner. The deployment process for supply chain technologies remains much shorter.
In every scenario, companies will question which supply chain management technology is most suitable for them, especially with numerous emerging options. Companies will review long- and short-term advantages and decide on their business goals, financial ability, integrations, ease of use, and how those technologies will affect their sustainable supply chains.
Top 5 technologies in supply chain management
1. Internet of things
For many small and medium-sized companies, IoT remains a distant vision in business evolution. Companies already existing on the market and remaining SMBs are struggling with many issues IoT can solve in the transportation, supply chain, and logistics industries. That matter of fact is to find a place for the successful application of IoT cost-effectively. Companies such as Volvo, the car producer belong to leading companies in this area, and have already implemented IoT solutions in their supply chains, using these technologies to streamline operations. They have actually used IoT to increase the traceability of spare parts.
McKinsey research predicted that by 2030, the application of IoT in supply chain management (SCM) could enable $5.5 trillion to $12.6 trillion in value globally. This includes the value captured by consumers and customers of IoT products and services.
The numbers are pumped up artificially, but we can be sure that there are low-hanging fruits for supply chains that want to gain a competitive advantage with low investment. Why low investment? It's because, despite many companies still recognizing technology adaptation as an expensive investment, it can be easier with custom software development.
Custom software development solutions and investment in IoT don't have to consume many resources. Especially when it comes to implementation based on MVP. We've learned from our experience that it's the most suitable way of adapting new technologies, such as IoT, for small and medium-sized businesses.
You can, for example, start small to see the pain points of the entire project. You can decide if the solution is suitable for now or just leave it in the experimental phase to keep a competitive advantage in your offering for the future.
That's right. Being an early adopter of new technologies allows you to use it as a competitive advantage in your offering when it comes to contracting new customers. Simply put, companies just are more eager to work with innovative businesses.
Here is an example of use cases of IoT in the food supply chain:
Significant advances in food monitoring technologies in supply chains have been made in recent years. The evolution has been important, from basic labeling systems such as barcodes to advanced Industry 4.0 solutions integrating AI, IoT, big data, sensors, and blockchain.
For example, sensors can now monitor grain stored in silos. In real-time, they track vital factors such as temperature, moisture, and air quality. It ensures optimal conditions to prevent mold, bacteria, and insect damage. IoT systems enable remote monitoring and automated alerts based on pre-set thresholds.
2. Artificial intelligence
We must stick to AI in our Top 5 tech in SCM as it is rapidly evolving, particularly considering that a lot of manual work in the Supply Chain will likely be removed within a decade. An easy way of adapting AI has been to point out that its usage has increased by 270% within the last three years!
Speaking about AI agents and apps, we need to mention the benefits of early adopters again. According to McKinsey, successfully implementing AI-enabled supply-chain management has enabled early adopters to improve logistics costs by 15 percent, inventory levels by 35 percent, and service levels by 65 percent compared to market competitors.
Need help with artificial intelligence software development?
Learn how we can boost your logistics processes
Explore moreAnother useful hint is that the global market for AI in the supply chain industry is expected to be over $20 billion by 2028, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 20.5%. Well, it's hard to neglect such a factor.
We have steadily observed that companies are increasingly willing to integrate artificial intelligence into their supply chains. However, they remain very cautious regarding AI as something that can fully replace their traditional business approaches.
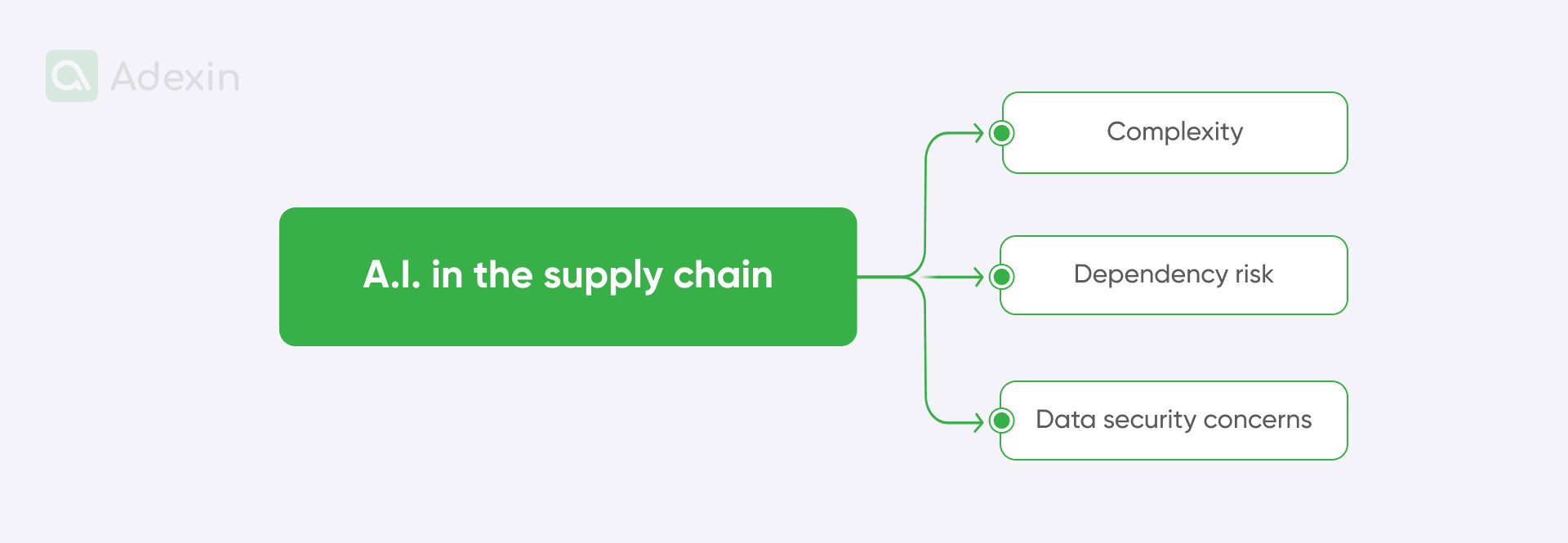
We observe companies are cautious about AI in the supply chain for three main reasons:
Complexity. A.I. systems can introduce complexity into supply chain processes, making them harder to understand and manage.
Dependency risk. Excessive reliance on AI without adequate fallback mechanisms can lead to vulnerabilities. If AI systems fail or encounter errors, they can disrupt supply chain operations.
Data security concerns. Artificial intelligence heavily relies on data. Therefore, it's clear that any breaches or compromises in data security could expose sensitive supply chain information.
Two examples of artificial intelligence in the supply chain:
Demand forecasting and planning. Artificial intelligence is powering forecasting engines, enabling interactive analysis of shipping data. U.S. industrial goods distributors use A.I. solutions to move toward dynamic planning and improve collaboration with suppliers and retailers.
Inventory management. Artificial intelligence improves logistics management optimizes inventory turnover and reduces inventory shortages. With an A.I. solution, supply chain logistics companies can reduce inventory by 43%. Artificial intelligence often employs more advanced technologies, such as drones, to photograph inventory in warehouses and obtain a clear view of real inventory.
3. Augmented data Intelligence and data analytics
The phrase sounds awkward, but it has become a significant trend in supply chain technologies because an augmented approach is needed to get the most out of the market. You cannot rely on partial data; you can employ some statistics to gain a clear and holistic perspective on forecasting demand. So, Data Intelligence has now evolved into Augmented Data Intelligence.
What does this mean? Frankly speaking, it's about improving continuous decision-making in supply chains. Companies are integrating multiple technologies to enhance data intelligence. Together, they speed up sophisticated data processing and provide valuable insights, forecasts, and recommendations.
Augmented Data Intelligence is about powering up data and analytics technology, which is based on platforms these days. According to data from Gartner, they expect that by 2025, 70% of organizations will be compelled to shift their focus from big to small and comprehensive data to leverage available data more effectively. It's all about reducing the required volume or extracting more value from unstructured, diverse data sources. So, again, a good data source is about data source integration.
From firsthand experience, we know that our customers in the supply chain heavily depend on quality data. We always provide this assurance to our customers by focusing on developing exact solutions based on quality written code. It is crucial when developing customized software solutions for supply chain companies that depend on data.
A good example of our involvement in such a project is our participation in a shipping document management platform project, where data management is based on workflows that rely on slick code. By using common sense when participating in any project, we know that this is a way to minimize the risk of unforeseen events and problems with the continued performance of the platform.
Examples of augmented data Intelligence and data analytics in the supply chain:
In supply chain management (SCM), analytics provides valuable information that enables organizations to make strategic decisions. You can optimize processes, reduce costs, improve visibility, and create a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
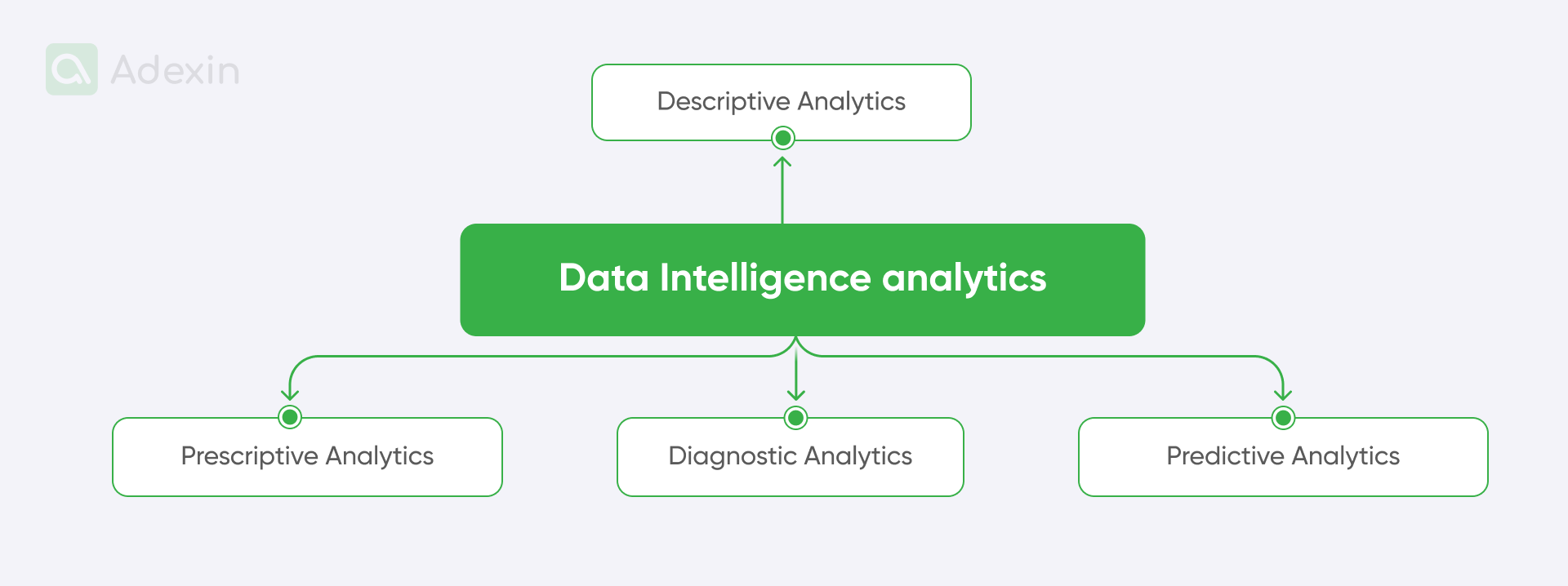
Traditional augmented data Intelligence analytics, performed by analytical software platforms, can be broadly categorized into four types:
Descriptive analytics. Describes past events and summarizes historical data to provide insights and trends. Examples can be found in the supply chain's sales and financial reports.
Diagnostic analytics. Its purpose is to examine why something happened in the past. This type of analysis attempts to identify the causes of certain events or patterns. Examples include root cause analysis and performance analysis.
Predictive analytics. Its goal is to predict future performance based on historical data using statistical algorithms and machine learning models. Examples include sales forecasting and demand prediction.
Prescriptive analytics. Recommends actions to optimize results by combining historical data, predictive models, and decision analysis. This provides decision support systems, logistics technology, and optimization models.
4. Warehouse automation
Moving around the U.S. or E.U. market, we encounter many companies already embracing automation in warehouses and making it a reality. It's just one of the many trends already in implementation. However, it never stands alone; IoT, analytics, and artificial intelligence often complement it.
According to McKinsey data, the overall automation market is growing rapidly. Some expert sources predict that robot shipments will increase by up to 50 percent each year through 2030. It translates to warehouse automation growing by more than 10 percent annually, which is remarkable when considering the global scale.
Custom software development is crucial in this matter. We have seen this through years of cooperation with supply chain companies that directly integrate their warehouses with supply chain operations. We observe this widely among companies that are implementing warehouse management systems and fleet management systems together.
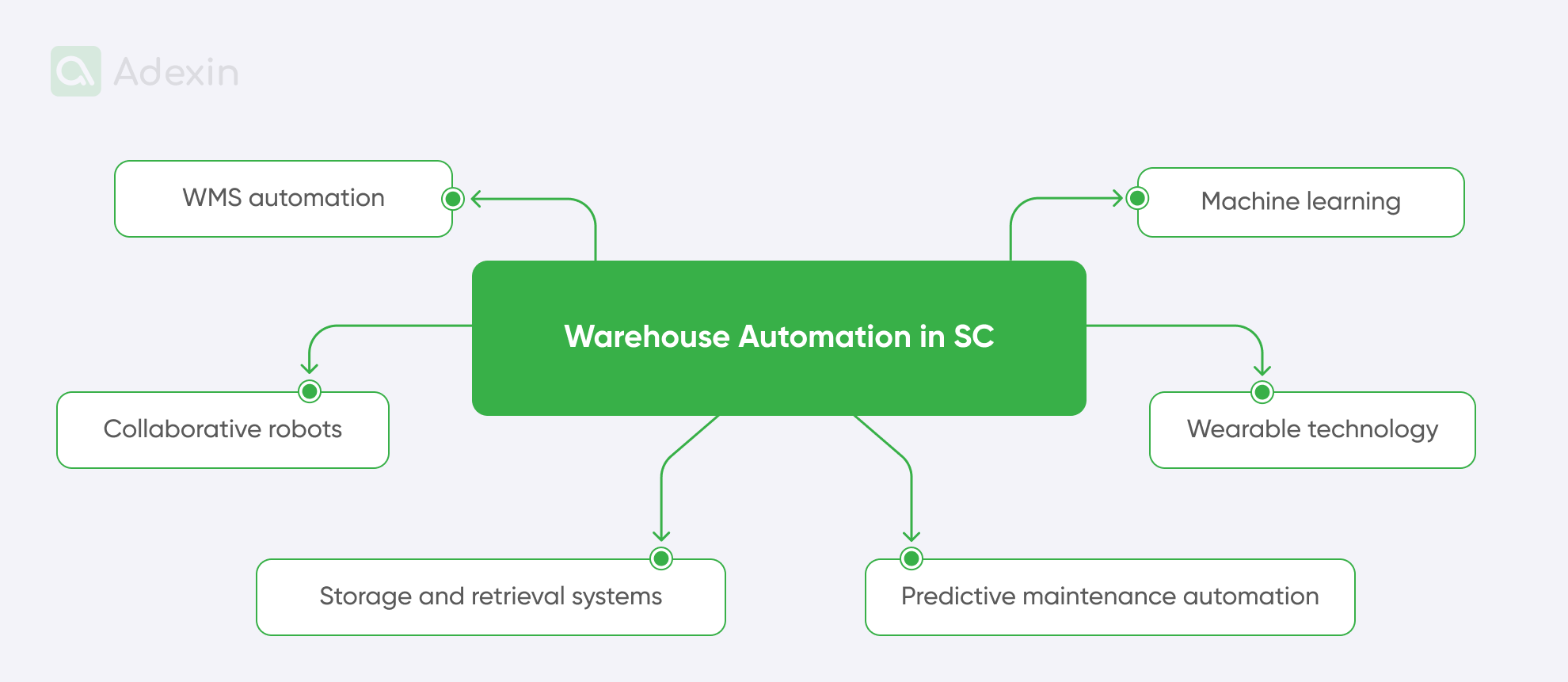
Example of warehouse automation in the supply chain:
WMS automation. These automations mainly occur in Warehouse Management System (WMS) software. It covers tasks such as automatic inventory tracking and shipping rates.
Machine learning. Using artificial intelligence (AI) programs and algorithms, machine learning improves specific warehouse management functions.
Collaborative robots. These robots, also known as co-bots, are designed to collaborate with workers. They are responsible for increasing efficiency and productivity while minimizing errors.
Storage and retrieval systems. Using machines such as conveyor belts and product lifters, companies can store and retrieve products from inventory.
Wearable technology. Smart glasses and similar products integrate augmented reality to help maintenance teams and inventory workers navigate warehouses more efficiently.
Predictive maintenance automation. Monitoring internal and external systems constantly. These automation detect potential problems and make quick repairs to prevent costly downtime.
5. Robotics in logistics technology
Integrating robots into logistics enhances the speed and accuracy of supply chain operations while minimizing human error. Robots outperform workers in terms of work time and productivity.
A significant advantage for companies is replacing human manual work, thereby increasing overall productivity with data analytics-based accurate measurements. Automating robotic processes enables the supply chain to decrease human involvement and identify and eliminate inefficiencies throughout the network.
Similar to warehouse automation, Robotic process automation (RPA) facilitates smooth operations around the clock, enabling managers to continuously optimize efficiency. With the help of artificial intelligence, RPA is similar to warehouse automation.
According to a McKinsey survey, 23% of supply chain respondents plan to invest more than $500 million in automation and robotics. The 2022 McKinsey Global Industrial Robotics Survey indicates that among the industrial sectors surveyed, retail and consumer goods are expected to be the largest automation spenders over the next five years, with the automotive industry accounting for 8% of the total.
Automation and robotization strictly depend on custom software. We know what kind of investment is required. Here are factors that improve robots with custom software based on our internal experience:
Examples of robot applications in the supply chain:
One of the most hazardous tasks in distribution centers involves racking, staging, and placing pallets on racks, posing significant risks to employees. To mitigate these dangers, robots have been introduced to take over these roles.
A perfect example is an intelligent robot with vision, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and grasping technology. This robot can automatically load and unload pallets without the need for pre-programming. It can also reduce the need for workers to engage in hazardous tasks such as stacking pallets in racks or stacking and placing pallets on racks.
Automated storage and retrieval systems that use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms can accurately process orders without human intervention. Compared to manual picking methods, these automated systems can increase throughput by 30% to 40%.
Need help with supply chain software development?
Learn how we can boost your business processes
Explore moreSummary of supply chain and technology
For small and medium-sized companies, the strategic implementation of new technologies such as IoT should begin with a methodical approach. Starting small to identify pain points and assess suitability before full-scale deployment. Early adoption of these technologies provides a competitive advantage in attracting customers. No company should underestimate that statement and approach.
The bottom line is that the strategic adoption of new technologies combined with customized solutions enables companies to thrive in a competitive landscape. You can deliver superior service and maintain market leadership very easily with MVP projects. Do you want to learn more? Do you want to see where Adexin has stepped up to help companies digitally transform their business with custom software development? Contact us today, and let's see where we can find common sense and support your efforts.

