Conventional air freight forwarders are under increasing pressure to digitize. Not many of you may know, but until now, only 60% of all carriers offer online registration. This also comes from the path that in markets like Belgium, many single truck owners serve as carriers. In Belgium, more than 10,000 companies transport goods by road, using more than 80,000 trucks and vans. It was also mentioned during one of the presentations on Transport & Logistics made by Philippe Degraef, Director of Febetra.be from Brussels. Compared to the US market, there are 13.5 million registered trucks. Of that number, 2.97 million are tractor-trailers, and 10.5 million are single-unit trucks (a.k.a. straight trucks). So, it's clear that there is huge competition and massive potential for development.
Companies in the transportation industry are facing competition from several fronts. These are digital shipping specialists, full-service digital freight forwarders, and carriers striving constantly to improve their digital business. A prediction made by McKinsey.com is that digital technologies will reduce costs and rates in the air freight forwarding industry based on digital development. It was stated that 10 to 15 percent of today's profit pool will go into customers' pockets. It means that carriers and customers can benefit from digital transformation and technology, such as zero carbon emissions vehicles, so then less diesel-powered cars.
This article looks at the digital nature of business models that are creating new opportunities to enter the industry and how transportation companies are evolving. So, it covers a bit of everything, with great reference to our knowledge about digital transportation and direct experience in the supply chain. Let's see what drives innovation today!
What is digital transportation?
Digital transportation is a way of converting manual-based processes into digital ones. For example, handling shipments 30 years ago by carrier was supported by paperwork and calls made by the transport coordinator and shipper in the office or the so-called Control Tower. Today, most of the job is done semi-automatically, with the most frequent tasks performed by highly advanced transportation software and a well-planned process based on a digital workflow. Along with technological advancements such as GPS, telematics, software, and predictive analytics, transportation has become more accurate in spending and, thus, more cost-effective.
For example in the transport sector, the contactless card system for passengers entering the public bus has significantly reduced operator costs in public transport. Along with other initiatives, it has diminished TfL's costs spent on revenue collection from 15 percent to 8 percent. TfL expects that, over time, this share will drop to 6 percent as more and more passengers adopt the contactless system.
There is no doubt that rapid technological change and evolving consumer needs are driving digital transformation. Logistics and transportation companies need to accelerate the development of data-driven business models to capitalize on new opportunities. However, 65% of executives in these industries remain calm about new market entrants and technology. So, how did that happen, then? Does digital transformation not pose a challenge and factual risk? No, that could be nothing more than a disguised conclusion. The fact is that digital transformation is on its way, and governance and entities are pushing towards it because it is environmentally friendly and cost-effective. Since logistics and transportation operate on very narrow margins, we cannot neglect this trend. Let's remember that each pool is governed by its own rules.
The scope of digital transformation in transportation
Digital transformation has brought significant changes to the transportation industry, transforming various aspects of transportation operations. Since road transportation includes two major segments, trucking and CEP, the transformation on the digital curve is evolving based on them. Trucking is a larger segment that includes long-haul transportation and distribution of goods over 30 kg. CEP focuses on the delivery of smaller cargo up to 30 kg, especially for last-mile deliveries.
We cannot remember that vans and trucks are used in other logistics segments, and trucking and CEP are the main growth drivers. So, considering these two segments, three trends have been observed that are driving changes in the logistics industry over the next decade. These three trends can more narrowly describe the scope of digital transformation:
Technological advances. Automation is expected to reduce vehicle costs by 35-50%, benefiting OEM customers and allowing them to capture some of that value. Huge impacts are having here also electric vehicles. This is all while connected services and future technologies such as drones continue to increase operational control and value.
Stricter regulations. Increased regulatory requirements will focus on sustainability. We see this, especially in last-mile logistics, where environmentally friendly solutions will become essential for companies to remain competitive.
Changing consumer expectations. Consumers increasingly seek personalized products and services that offer flexibility. So, transportation should be agile and adjust with delivery times and locations tailored to their needs.
Thinking more practically about the scope, we should outline each area. Here are some key areas where digital transformation has made a substantial impact recently:
Data-driven insights and optimization
By leveraging advanced data analytics, transportation companies can forecast demand patterns, optimize routes, and anticipate disruptions, enabling greater operational efficiency and cost savings. These tools are vital as road-based logistics revenue is expected to increase by 60% by 2025, aligning with the sector's expansion.
Real-time tracking tools allow companies to monitor shipments and respond swiftly to disruptions, which is key to meeting consumer demand. As same-day delivery options grow, 10% of German consumers report they would pay an extra €1 or more for this service, indicating a premium for instant convenience.
Autonomous vehicles, robotics, and autonomous aerial vehicles
Automation, including electric vehicles and robotic warehousing, rapidly reshapes logistics. Automation alone is projected to account for 60% of truck revenue growth from new revenue pools. By 2025, 33% of newly delivered premium trucks in Western markets are expected to feature Level 4 automation. This is what's contributing to a projected 50% growth in the profit pool for medium- and heavy-duty trucks, let's remember it won't be possible without smart charging infrastructure.
Internet of things (IoT), telematics, and digital technologies
IoT sensors and RFID systems monitor real-time data on fuel consumption, vehicle health, and maintenance needs, helping managers streamline operations and reduce downtime. As demand for additional transport capacity drives 40% of trucking revenue growth, intelligent and high-speed fleet management ensures fleets meet this demand efficiently. This all offers revolutionary possibilities.
ECommerce integration and digital technology
The eCommerce boom has fueled demand for fast, efficient delivery services. As last-mile logistics grows by 8% annually, digital platforms streamline order processing, inventory, and delivery management, meeting consumer expectations for speed and reliability. By 2025, 25% of the B2C market for courier, express, and parcel (CEP) services is expected to be same-day delivery, driven by consumer demands for convenience.
Cloud computing, AI, and business processes
Cloud technology offers scalable, flexible options for managing transportation operations, reducing IT costs, and enabling global data access. Cloud-based applications support the industry's shift toward capacity as a service, which 49% of OEM executives view as a promising business model for the future.
AI enhances route optimization, resource allocation, and operational efficiency, helping companies adapt to the 4% annual rise in long-haul trucking demand. Artificial intelligence is also crucial for managing the anticipated 50% growth in profit for medium- and heavy-duty trucks by 2025, offering insights that drive better decision-making.
Collaborative transportation networks and digital documentation
Digital platforms enable cross-company collaboration, improving coordination and efficiency across the logistics ecosystem. Shared resources and data enhance service quality and help lower operational costs, an essential aspect as logistics adapts to new business models.
Electronic documents and digital signatures streamline processes, reducing paperwork, errors, and processing time. This shift is critical in an increasingly digital environment, ensuring operations remain fast, secure, and compliant.
Data security, privacy as new digital form
As logistics digitizes, cybersecurity is a top priority to safeguard sensitive information from cyber threats. With 51% of logistics executives aiming to retain data in-house, secure data management practices are crucial for protecting customer and operational data.
5 trends of transformation in logistics and transportation
The transportation industry is undergoing a significant digital transformation driven by rapid technological advances and changing consumer behavior. This is the future of transportation and this transformation presents numerous trends and opportunities that could transform the transportation industry as we know it. Here are some key trends and opportunities for digital transformation in transportation:
1. Interconnected vehicles and IoT integration
Such vehicles, infrastructure, and central control systems can communicate with each other. This connectivity improves traffic management, enhances safety with collision avoidance systems, and provides real-time data for better decision-making.
2. Autonomous vehicles and automation
Autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, are at the forefront of transportation innovation. While fully driverless cars are still in the testing phase, automation is already being integrated into various transportation modes, such as automated drones, trucks, and trains. This trend has the potential to revolutionize logistics and last-mile delivery, so to speak home delivery. It may also put less attention on long-distance transport in the future.
3. Mobility as a service (MaaS)
MaaS is a concept that offers a seamless and integrated transportation experience. Users can plan, book, and pay for various transportation modes through a single digital platform, such as buses, trains, ride-sharing, and more. MaaS promotes sustainable transportation choices and reduces traffic congestion.
4. Smart infrastructure and traffic management
Intelligent traffic management systems use real-time data to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance road safety. Examples of this trend are bright traffic lights, adaptive traffic control algorithms, and bright signage.
5. ECommerce and last-mile delivery innovations
The growth of eCommerce has spurred innovation in last-mile delivery. Drones, delivery robots, and driverless cars are being explored to expedite deliveries and enhance customer experiences.
What are digital transportation examples?
Digital transformation is a key force in transforming transportation across different industries. In the rail public transport industry, for instance, London's Oyster card system has transformed commuting in the city, allowing passengers to seamlessly use a single contactless card. On the commercial front, companies such as Uber have disrupted traditional cab services by using mobile apps to hail rides, changing the way people travel. In a more recent example, DHL's use of IoT devices and real-time tracking software in logistics operations demonstrates how digitization is increasing supply chain visibility and efficiency.
There are countless more examples. We can bring to light one related to UK public transport. A survey of London rail passengers revealed that 43% prioritize reduced delays and cancellations, while 30% each desire increased train capacity and frequency. To address these needs, transit agencies are turning to real-time predictive analytics. By leveraging data from Automatic Fare Collection (AFC) systems, researchers are developing models to predict:
Train arrivals within 15-30 minutes
Passenger origins and destinations
Train load
These predictions empower transit agencies to make informed decisions and implement strategies in real-time, such as adjusting schedules or deploying additional resources. This proactive approach enhances system resilience and improves overall passenger experience.
Also, we can mention that FIDELITONE successfully integrated with a company’s ERP to create real-time visibility through the FIDELITONE Partner Portal. FIDELITONE is a 3PL Order Fulfilment and Last Mile Delivery that takes care of inbound logistics and other processes in the supply chain. They’ve implemented customer surveys and a weekly scorecard to keep a pulse on performance and satisfaction. This turnkey solution addressed every aspect of last-mile delivery and helped track better processes all over the network.
Obviously, we couldn’t miss development related to mobile apps and how important role these play for innovative transportation solutions. Having direct experience in the transportation industry, we have also had many cases where we supported the supply chain. For example, we have developed a mobile app for truck drivers that has completely changed business operations in a transportation company. Benefits such as better time management and digital document handling are only a small glimpse of how mobility is changing the industry.

The next example is coming with autonomous electric vehicles, self-driving taxis, and automation. Significant investments were made in 2010 to transform basic work units into robust, highly available, fault-tolerant, and cost-effective products for the market. This long incubation period was necessary to ensure safety, robustness, and service performance in the US market. Some solutions have achieved regulatory, public, and industry acceptance and require comprehensive safety validation. But it wasn’t so easy. What happened between 2017-2018 after an Uber robo-taxi prototype in Arizona collided with and killed a pedestrian, has led to strengthened restrictions in development. Moreover, several Tesla drivers were killed while using the AutoPilot feature, and there wasn’t any exception for Tesla cars. These incidents highlighted the challenges of shared human-machine control and underscored the need for fully automated vehicles.
Another case where the tests are on the way is Waymo. They’re operating a fleet of around 600 AVs, mainly in Phoenix, and partnering with UPS for local package movement. Moreover, other businesses, such as Walmart and Domino’s Pizza are testing autonomous grocery delivery in Houston with NURO.
There are many examples today that underscore how companies are leading the way in using digital technologies to redefine transportation standards that are bringing a major shift in transportation worldwide.
What are the business opportunities for digitalization in transportation?
Digital transformation in transportation represents a promising landscape of opportunities. With the aforementioned integration of advanced technologies such as autonomous vehicles, intelligent traffic management systems, and mobility as a service (MaaS), the transportation industry has the potential for significant improvements. These innovations can lead to a variety of benefits that can affect overall performance:
Digital transformation in logistics
A great illustration of digital technology and transformation in the logistics industry is the business of DHL, a well-known global logistics company. DHL has used cutting-edge digital technologies to redefine the way it manages and optimizes its logistics processes. The digital transformation initiative included the implementation of IoT (Internet of Things) and predictive analytics, simultaneously providing significant benefits to the logistics industry and DHL itself.
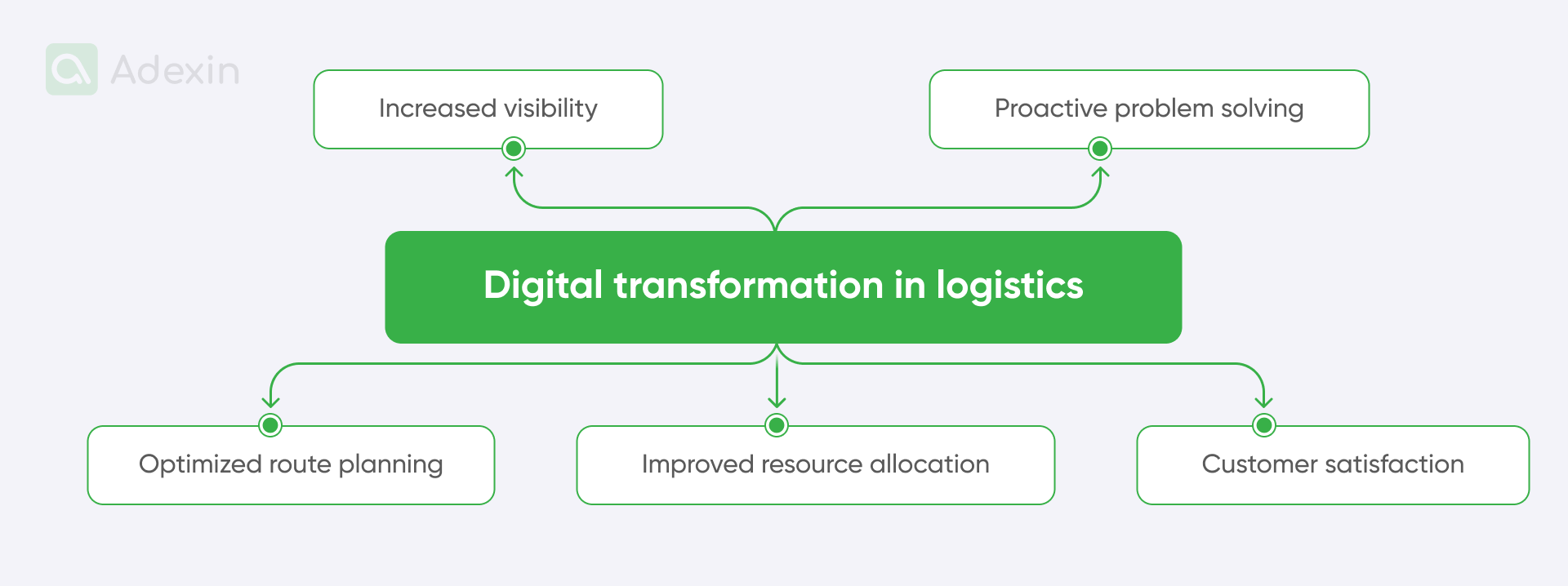
Let's take a look at the key elements of digital transformation in the DHL:
Increased visibility. By integrating IoT sensors into shipments, DHL can provide real-time visibility into the location, status, and condition of goods throughout the supply chain, enabling customers to accurately track shipments.
Proactive problem-solving. With predictive analytics, DHL can anticipate potential disruptions or delays in the supply chain and take preventive measures to mitigate risks, ensuring timely and efficient deliveries.
Optimized route planning. DHL uses data analytics to analyze historical and real-time traffic data, enabling optimal route planning for its fleet of vehicles. This reduces delivery times and fuel consumption.
Improved resource allocation. DHL's digital transformation has led to more efficient allocation of resources, such as vehicles and manpower, based on demand patterns and operational needs, thereby increasing overall efficiency.
Customer satisfaction. The transparency and accuracy facilitated by DHL's digital solutions have significantly improved customer satisfaction by providing timely updates, reducing delivery errors, and offering personalized delivery options.
Digital transformation in public transport
A clear example of digital transformation in the transportation industry is London's Oyster card system. By implementing this contactless payment system on various public transportation modes, Transport for London (TfL) has experienced several notable benefits:
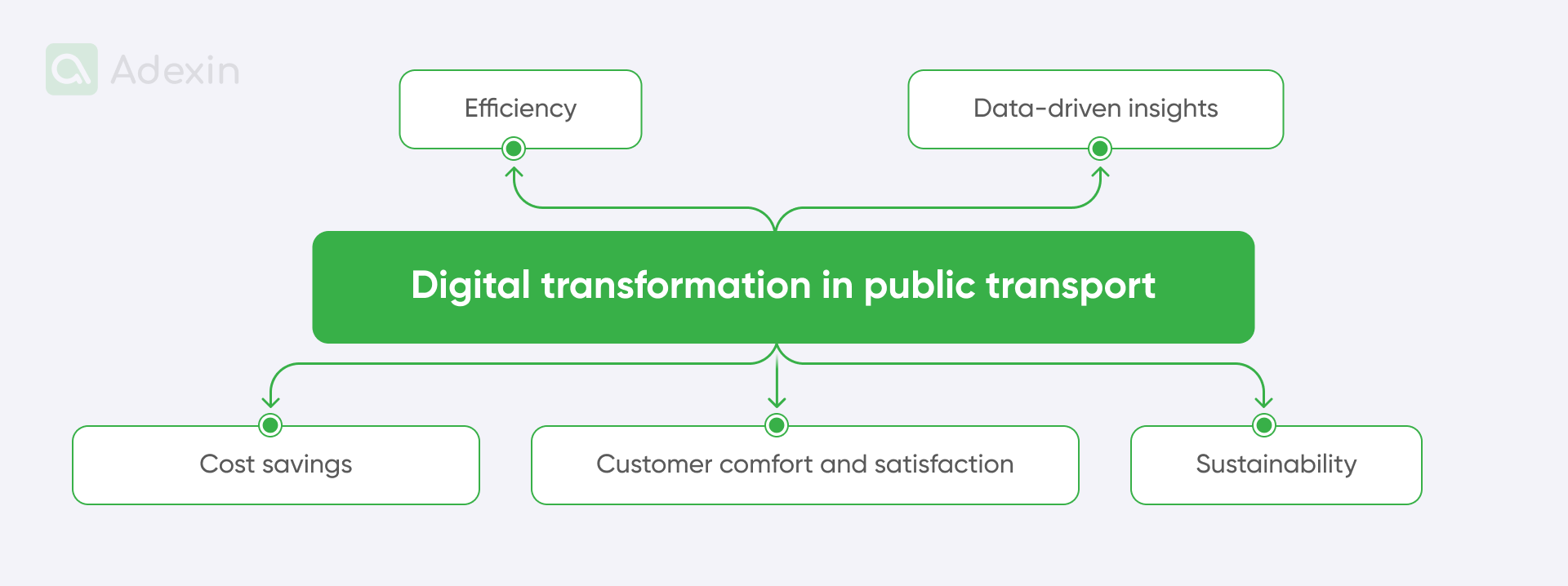
Let's take a look at the key elements of digital transformation in the TfL:
Efficiency. The Oyster card eliminates the need for paper tickets, streamlining the passenger boarding process and reducing the time spent on ticket transactions.
Data-driven insights. The system collects valuable data on travel patterns, peak hours, and popular routes. TfL can analyze this information to optimize schedules, efficiently allocate resources, and plan future infrastructure improvements.
Cost savings. Oyster cards offer discounted fares compared to single paper tickets, encouraging passengers to choose more economical travel options. This encourages more frequent card use and helps reduce cash-handling expenses.
Customer comfort and satisfaction. Passengers enjoy hassle-free travel as they can easily reload their Oyster cards online or at various kiosks. This convenience encourages more rides and increases customer satisfaction.
Sustainability. By reducing reliance on paper tickets and streamlining operations, the Oyster card contributes to less paper waste and a greener transportation system, aligning with broader sustainability goals.
Digital transformation in commercial transport
A key example of digital transformation in commercial transportation and the designer of flying taxis is Uber, the ride-sharing giant. Uber's innovative platform has brought several significant benefits to the industry.
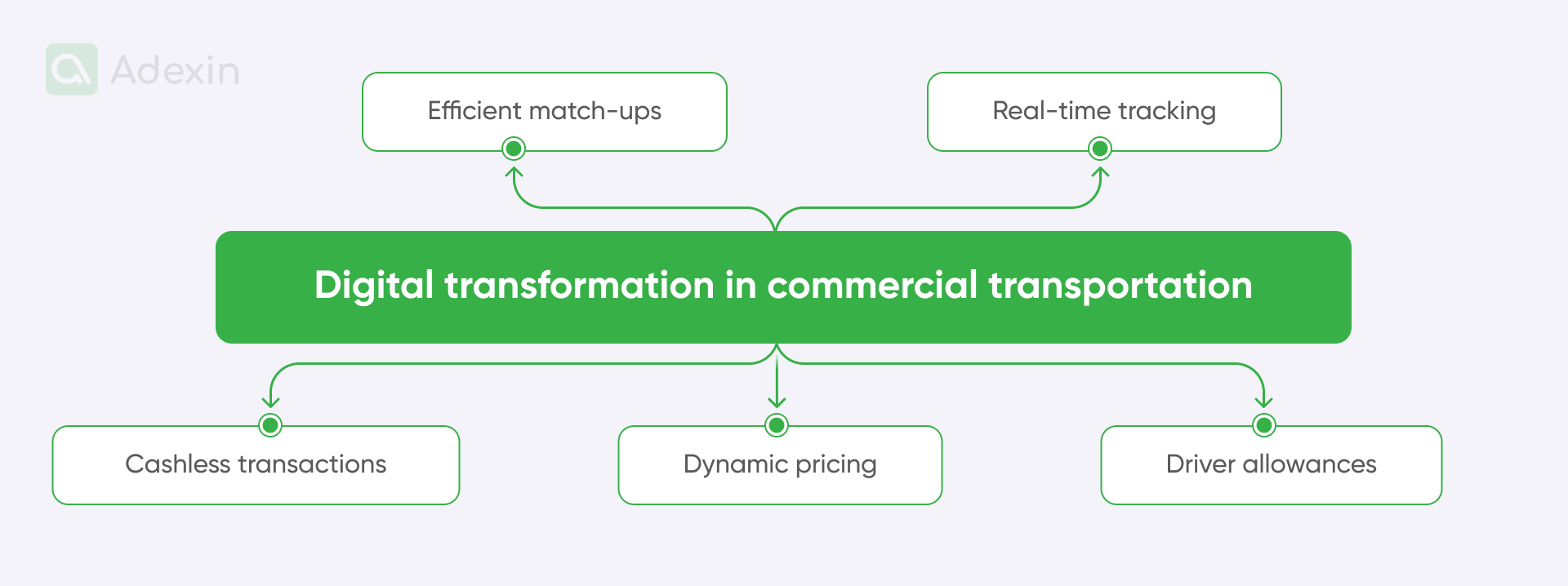
Let's take a look at the key elements of digital transformation in the Uber:
Efficient match-ups. Uber's app effectively connects drivers with passengers based on location, reducing driver idle time and minimizing passenger waiting time.
Real-time tracking. Passengers can track the location of their assigned vehicle in real-time, increasing transparency and providing a sense of security.
Cashless transactions. Uber's digital payment system eliminates the need for cash transactions, providing a smooth and secure payment experience for both drivers and passengers.
Dynamic pricing. Uber's pricing model adjusts fares based on demand, encouraging more drivers to be available during peak hours and balancing supply with demand.
Driver allowances. The platform offers drivers flexibility, allowing them to work on their own terms. This opportunity has attracted a diverse pool of drivers, increasing the availability of transportation options.
Today, Uber is developing a project of flying taxis with eVTOLs vehicles and also working on the Skyport infrastructure project. Yes, this is only the beginning of such developments and it’s a good way to zero-emissions vehicles, but the foundation has already been laid and we will most likely see flying taxis in real life.
Need help with digital transformation for your transportation business?
Learn how we can help you
Explore moreFinale takeaway
The future of transportation is digital. Using innovative technologies, we can create a more efficient transportation system. We now have the tools to remain more environmentally friendly and accessible. Adexin is committed to helping companies navigate this digital transformation and build a better future for transportation.
Looking at the latest industry developments, the transportation industry is undergoing a rapid transformation. The companies that adopt digital solutions into business processes will be the ones that thrive. Adexin can help implement the latest technologies to optimize operations. Contact Adexin today to learn more about our custom software solutions for the transportation industry.


